Design and enhancing the performance of a hollow core-based photonic crystal fiber sensor for alcohols sensing in the THz spectrum
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.4279/pip.170003Keywords:
Hexagonal photonic crystal fiber; Optical alcohol sensor; Relative sensitivity; Confinement loss; Effective area; THz wave transmissionAbstract
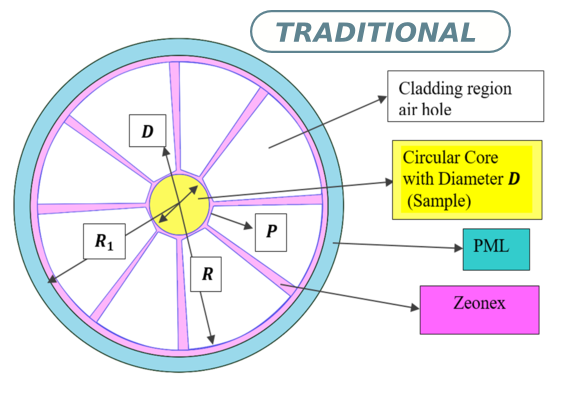
In this work, we explore a wheel-shaped hollow-core photonic crystal fiber (HC-PCF)-based optical alcohol sensor that operates in the terahertz (THz) region. We employ the finite element method (FEM) along with COMSOL Multiphysics software to simulate the structure and perform a numerical analysis of the model. In this configuration, alcohol analytes are integrated into the fiber's core. The results from the FEM simulation indicate that the proposed optical HC-PCF sensor achieves high sensitivity levels of 97.61\% for ethanol, 98.80\% for butanol, and 98.53\% for propanol, all at a frequency of 2.1 THz. The measured low confinement losses at 2.1 THz are $8.0696\times10^{-8}~\text{dB/m}$, $7.1966\times10^{-11}~\text{dB/m}$ and $3.6334\times10^{-10}~\text{dB/m}.$ Furthermore, the effective areas are $7.5911~\times~10^{-8}~\text{m}^2$, $7.8258\times10^{-8}~\text{m}^2$, and $8.0847\times10^{-8}~\text{m}^2$ for three types of alcohol. Additionally, we discuss the concepts of effective material loss, effective mode index, and total power fraction. Existing technologies can facilitate the fabrication of this proposed sensor. Moreover, we anticipate that the application of our fabricated sensor will extend to biomedicine, biosensing experiments, industrial applications, material research, healthcare, alcohol detection in drinks and liquids, and other THz communication technologies based on waveguides.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Jannatun Ferdous, Md. Dulal Haque, Mahfujur Rahman, Md. Selim Hossain, Md. Abubakar Siddik

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Authors agree to the PIP Copyleft Notice













